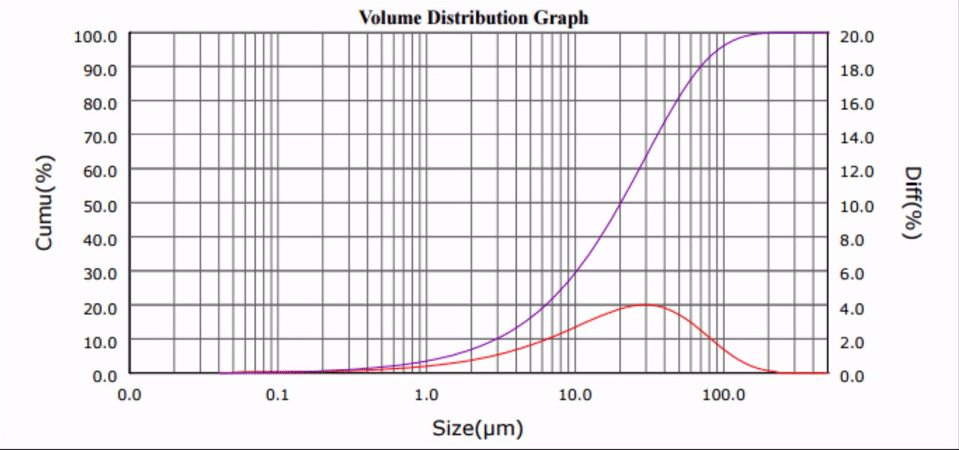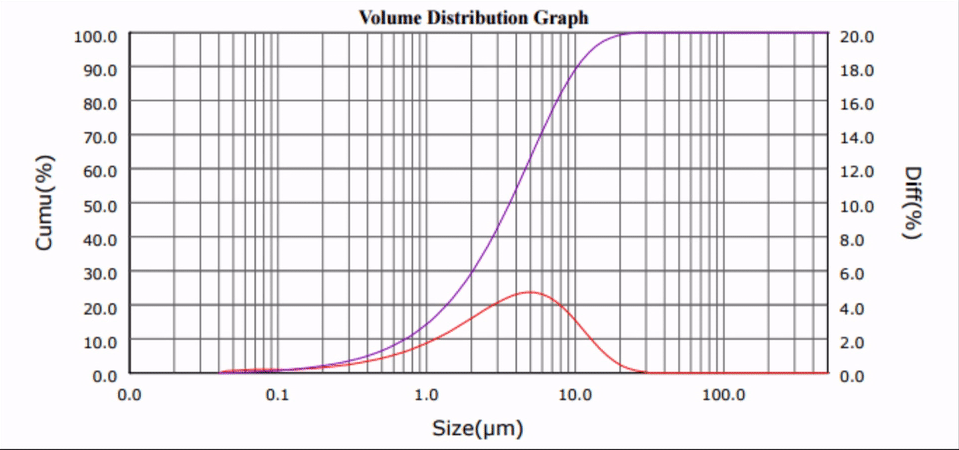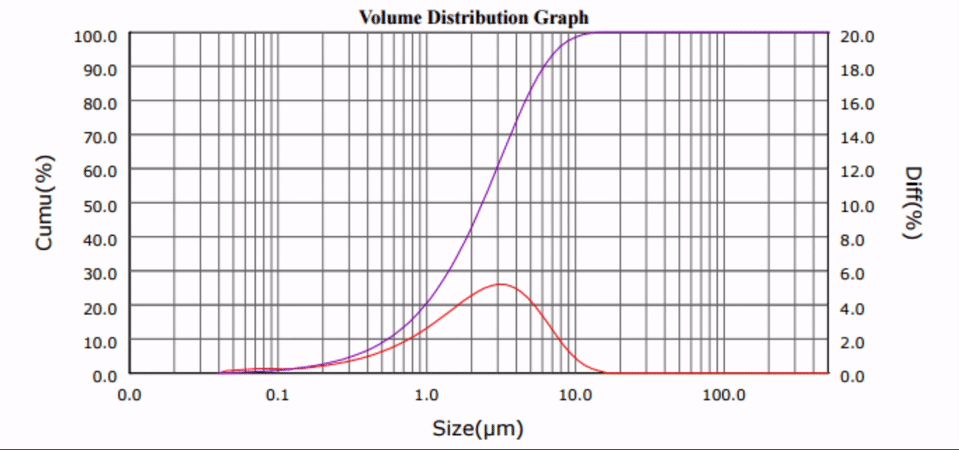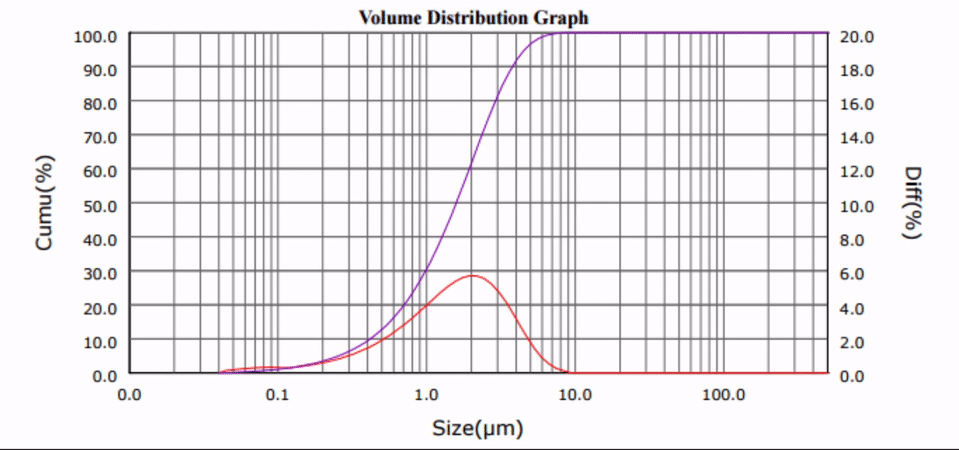
Cement, and its paved derivative, concrete, is a widely-consumed material in any modern society: residential walkways, recreational parks and building construction are just some of the many uses of cement. This year, upwards of 80 million metric tons of cement will be processed in the United States alone [1].
As a building and support material, the two most important qualities of cement are its compressive strength (the capability to withstand an inward load) and its workability (the propensity of the cement paste to be deformable and fluidized). Unfortunately, these two qualities are not independent of each other.
.jpg?width=1994&height=332&name=Logo%20Sonomechanics%20White%20No%20Shadow%20R_Final%20(1).jpg)