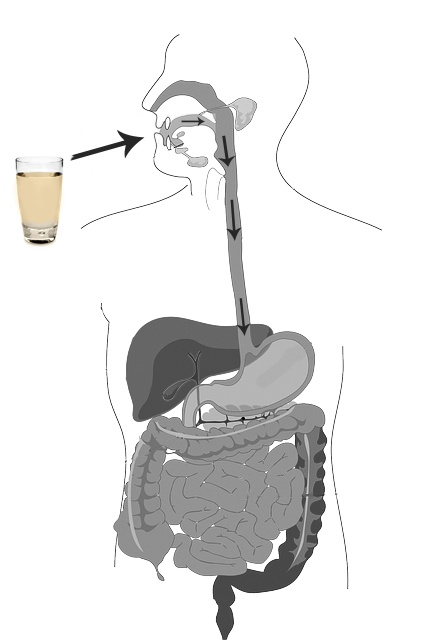
Recent years have seen major breakthroughs in how vaccines and antiviral drugs are formulated and manufactured. Nanoemulsions and liposomes are now widely used as vaccine and drug carriers because they can easily incorporate lipophilic (in the case of nanoemulsions) and hydrophilic (in the case of liposomes) bioactive compounds, stabilize substances that otherwise undergo hydrolysis, and significantly reduce side effects of potent drugs. For the past 14 years, Industrial Sonomechanics (ISM) has been conducting R&D and supplying its scalable ultrasonic technology to many companies in this field, including those using it in ultrasonic vaccine production and, more recently, in the development of SARS-CoV-
Vaccine and Antiviral Drug Production with ISM Ultrasonic Processors
[fa icon="calendar'] Apr 28, 2020 10:40:21 AM / by Alexey Peshkovsky, Ph.D. posted in Emulsion-based Products, Process Scale-up, Extraction
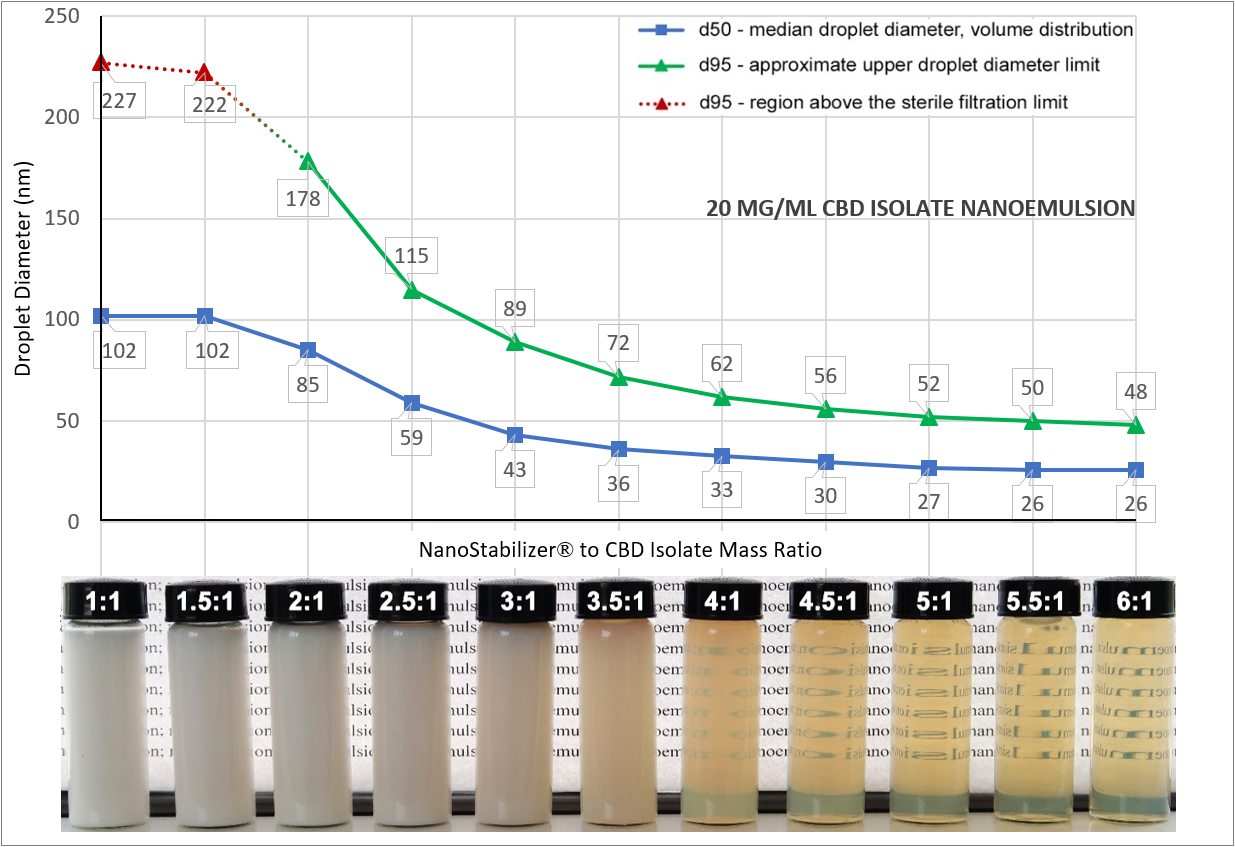
6 Frequently Asked Questions About All-In-One NanoStabilizer®-LT
[fa icon="calendar'] Feb 3, 2020 11:48:04 AM / by Alexey Peshkovsky, Ph.D. posted in Emulsion-based Products, Medical Cannabis
For the past two years, many businesses have been using our all-in-one NanoStabilizer®-LT to convert their cannabis extracts and other hydrophobic bio-actives into water-compatible, stable, translucent nanoemulsions. Most commonly, the conversion is done in order to enhance the bioavailability and accelerate the onset of action of cannabinoids and to infuse beverages without making them cloudy. Designed to work with Industrial Sonomechanics ultrasonic liquid processors, NanoStabilizer®-LT requires no formulation development experience and is compatible with a wide range of bio-actives, including most types of cannabis extracts and isolates, pharmaceutical ingredients, vitamins, essential oils, terpenes, etc. In this post, I provide answers to some of the most commonly asked questions about this popular product.
Presentation Recording, 2019 Cannabis Drinks Expo, San Francisco, CA
[fa icon="calendar'] Dec 3, 2019 9:30:00 AM / by Iva Gyurgina posted in Emulsion-based Products, General Announcements, Medical Cannabis
We are happy to announce that the recording of Dr. Alexey Peshkovsky's 2019 Cannabis Drinks Expo keynote presentation is now ready. In his talk, entitled "Water-compatible cannabis extract nanoemulsions: benefits, formulation development and production methodology", ISM President & Chief Scientific Officer covered several topics critical to the cannabis-infused beverage industry.
How to Formulate Cannabis Extract Nanoemulsions with a Long Shelf Life
[fa icon="calendar'] Oct 8, 2019 9:30:00 AM / by Shlomo Leibtag posted in Emulsion-based Products, Medical Cannabis
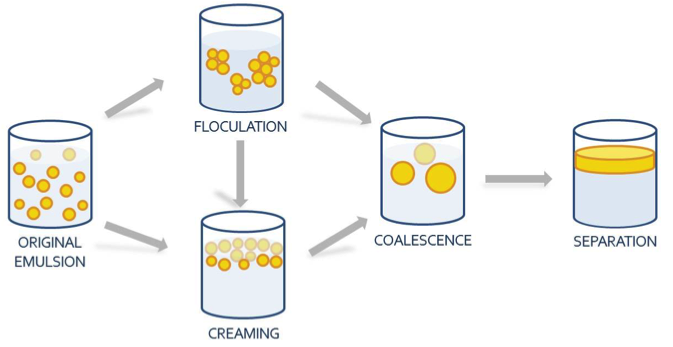
One of the primary concerns when formulating oil-in-water (O/W) nanoemulsions is the stability of the finished product. Destabilization of an O/W nanoemulsion can occur due to several physical, chemical or biological processes that deteriorate its quality over time. Understanding and avoiding these processes is paramount to ensuring that products based on cannabis extract nanoemulsions (a.k.a. "water-soluble" CBD and THC) have a long and predictable shelf-life. In this post, common nanoemulsion destabilization pathways will be described, along with the most effective strategies to avoid them.
Why Sterile-Filter Water-Compatible Cannabis Extract Nanoemulsions?
[fa icon="calendar'] Dec 3, 2018 10:23:58 AM / by Alexey Peshkovsky, Ph.D. posted in Emulsion-based Products, Medical Cannabis
Sterile filtration is an important post-processing step of ultrasonic nano-emulsification - a process that converts cannabis extracts and/or other hydrophobic bioactives into a water-compatible form. In this article, I will summarize the steps of the nano-emulsification process carried out with BHUT-based ultrasonic equipment and NanoStabilizer®-LT, list the main advantages of the resulting water-compatible nanoemulsions, and explain why sterile filtration is always necessary at the end. Answers to several FAQs will also be provided.
Managing the Bitter Taste of Cannabis-Infused Beverages
[fa icon="calendar'] Sep 18, 2018 9:00:00 AM / by Alexey Peshkovsky, Ph.D. posted in Emulsion-based Products, Medical Cannabis
We are frequently asked how to minimize the bitter taste of products made with cannabis extract nanoemulsions (a.k.a., water-soluble CBD and THC). Infusing beverages with CBD and/or THC-containing translucent nanoemulsions (ideally, averaging ~20 nanometers in droplet size diameter) offers a very convenient, discrete and effective consumption method. The infusion does not change the original appearance of the beverages while instantly enabling them to provide a very rapid onset of action and high bioavailability of cannabinoids as well as of any other incorporated active ingredients. With this pharmacokinetic profile, the experience a lot more similar to consuming an alcoholic beverage than a typical cannabis-containing edible, which provides a myriad of attractive options for the vendors and consumers. In many cases, however, the infusion results in a bitter taste, which can range in intensity from virtually undetectable to quite unpleasant and makes it important to understand and manage.
All-In-One NanoStabilizer®-LT Simplifies Making Water-Soluble CBD and THC
[fa icon="calendar'] Apr 10, 2018 9:00:00 AM / by Iva Gyurgina posted in Emulsion-based Products, Medical Cannabis
You do not have to be a scientist to make high-quality water-soluble CBD and THC! Industrial Sonomechanics' customers no longer need to develop their own formulations and production protocols for cannabis extract nanoemulsions. We are pleased to announce the launch of a new product: All-In-One NanoStabilizer®-LT. This convenient product can tremendously simplify the ultrasonic production of high-quality, translucent nanoemulsions of bio-active ingredients such as cannabis extracts. This product is designed to work in conjunction with our laboratory, bench and industrial ultrasonic processors, and comes with detailed, easy-to-follow instructions.
Ways to Consume Cannabis: How Water-Compatible Nanoemulsions Can Help
[fa icon="calendar'] Aug 20, 2017 9:00:00 AM / by Alexey Peshkovsky, Ph.D. posted in Emulsion-based Products, Medical Cannabis
There are many ways to administer medical and recreational cannabis, each with its own benefits and drawbacks. One common feature, however, is that only a certain (generally small) percentage of the consumed cannabinoid content, defined as "bioavailability", can be absorbed into the bloodstream with each method. This stems from the fact that cannabinoids are not water-soluble and, therefore, not readily compatible with the predominantly water-based human body. Water-soluble compounds such as ethanol, on the other hand, can be quickly and efficiently delivered to the bloodstream via a variety of alcoholic beverages, eliminating the need for other delivery methods. Wouldn't it be great if the same could be done with cannabis?
The Role of Carrier Oils in Water-Soluble CBD and THC Formulations
[fa icon="calendar'] Jan 28, 2017 11:37:28 AM / by Alexey Peshkovsky, Ph.D. posted in Emulsion-based Products, Medical Cannabis
This is a second article in the series on the principles of formulating water-compatible cannabis extracts and isolates, also known as water-soluble CBD and THC. The first article showed multiple advantages of nanoemulsions over the other two water-compatible formulation classes: microemulsions and liposomes. Here I will demonstrate the importance of using a carrier oil in your cannabis extract or isolate nanoemulsion. I will also explain how to select the proper carrier oil among the available choices.
Water-Soluble Cannabis Oils: Microemulsion, Liposomes or Nanoemulsion?
[fa icon="calendar'] Nov 24, 2016 9:00:00 AM / by Alexey Peshkovsky, Ph.D. posted in Emulsion-based Products, Medical Cannabis
Industrial Sonomechanics is launching a series of blog posts dedicated to describing the main principles of developing water-compatible cannabis extract formulations, also known as water-soluble CBD and THC. As explained in our earlier blog post, since medical marijuana extracts are oils and, as such, not soluble in water, they have to be specially formulated in order to become water-compatible and acquire the appearance of being water-soluble. There are three formulation classes that can provide this property: microemulsions, liposomes and nanoemulsions.
.jpg?width=1994&height=332&name=Logo%20Sonomechanics%20White%20No%20Shadow%20R_Final%20(1).jpg)